Reference frames
Small earth reference frame
To understand how the control system is working it is necessary to introduce the small earth reference frame. This name is chosen as an analogy to the geographic coordinate system, describing a position on planet earth: It makes clear to the reader that navigation methods, used on earth (like great circle navigation to find the shortest way between two points on the sphere) can also be used to navigate kites. The position of the kite and the ground station are measured in the "Earth Centered Earth Fixed" reference frame. The position of the kite relative to the ground station has to be converted into the "Wind Reference Frame" ($x_w , y_w , z_w$) as shown in Fig. 5.1.
The origin of the wind reference frame is placed at the anchor point of the tether and its $x_w$ axis is always pointing in the direction of the averaged wind velocity. To obtain the coordinates of the kite in the small earth reference frame its position is projected on the unit sphere around the origin of the wind reference frame. Now, the position of the kite can be described with two angles, the azimuth angle φ and the elevation angle β . The movement of the kite in the direction of the tether is determined by the winch controller and can be ignored by the kite controller. The objective of the flight path controller as described in this thesis is to fly the kite on a prescribed trajectory that is adapted to the wind conditions.
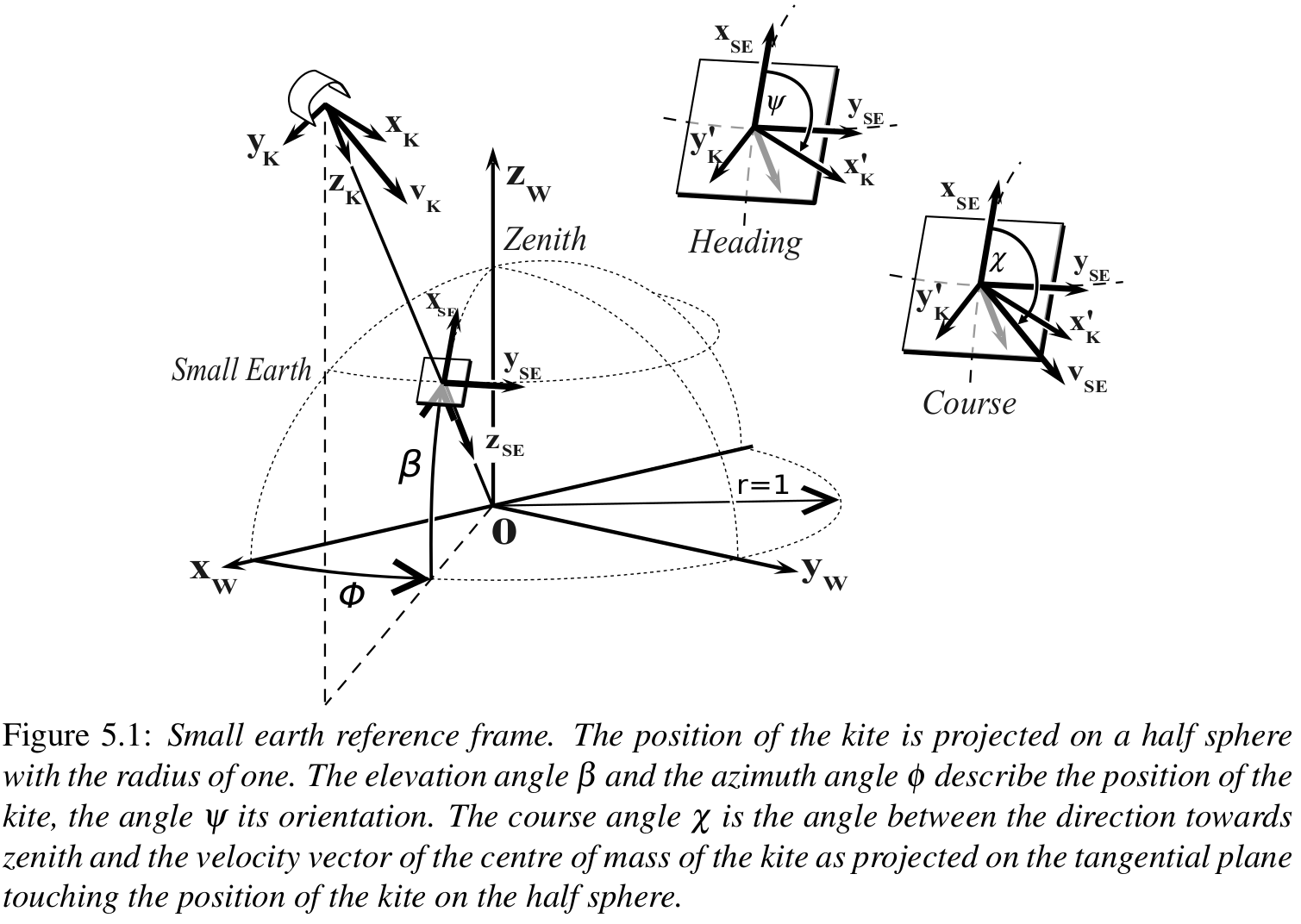
In Fig. 5.1 the vectors $x_k, y_k$ and $z_k$ define the body-fixed kite reference frame. In this chapter, the combination of the wing and the kite control unit (KCU) is seen as kite. The $y_k$ axis is defined by the vector from the left to the right wing tip, the $z_k$ axis is pointing downwards from the position of the kite parallel to the upper part of the tether, and the $x_k$ axis is orthogonal to $y_k$ and $z_k$ . The heading angle ψ is the angle between the direction towards zenith and the vector $x_k$ as projected on the tangential plane touching the position of the kite on the half sphere. If tether is not straight, $z_k$ and $z_{SE}$ are not aligned.
Fechner U. A Methodology for the Design of Kite-Power Control Systems. 2016. 212 p. https://doi.org/10.4233/uuid:85efaf4c-9dce-4111-bc91-7171b9da4b77